zMRI Lab (Zaiss)
Welcome to the research group Multimodal Imaging in Clinical Research!
We always offer exciting Bachelor, Master and PhD topics. If you are interested, please send an email to moritz.zaiss@uk-erlangen.de.
see current Potential Projects
1. Metabolic Imaging
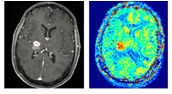
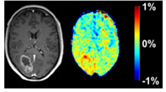
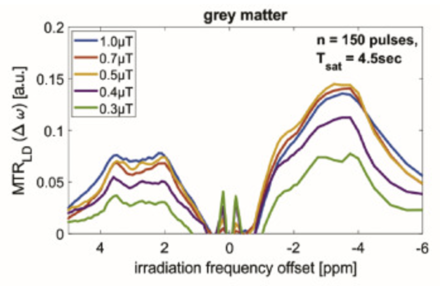
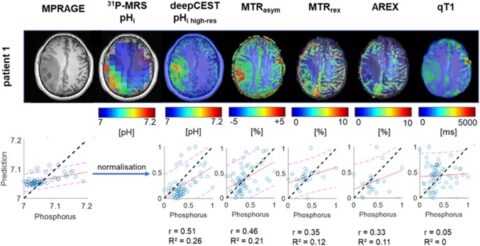
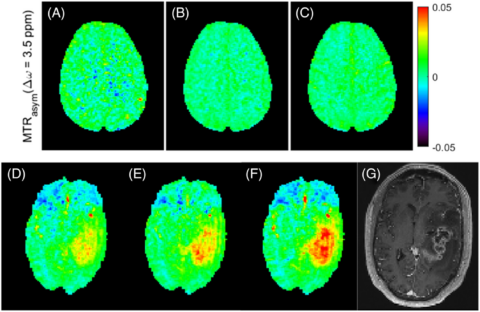
Chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI is a relatively novel MRI technique that is not yet in routine clinical use. CEST is able to provide a spectroscopic and molecular MRI contrast by using proton transfer of endogenous molecules that exchange with the abundant water pool. CEST generates a signal amplification of up to 3 orders of magnitude compared to MR spectroscopy.
The best studied effect to date is amide CEST MRI, which originates from backbone amides of endogenous proteins and peptides (3.5 ppm), also known as amide proton transfer-weighted CEST. Amide CEST at ultra-high fields yielded an astonishing spatial coherence with contrast-enhanced (ce) MRI. Glucose CEST allows detection of glucose uptake after injection making natural D-glucose a contrast agent.
2. Fast MRI – snapshot CEST
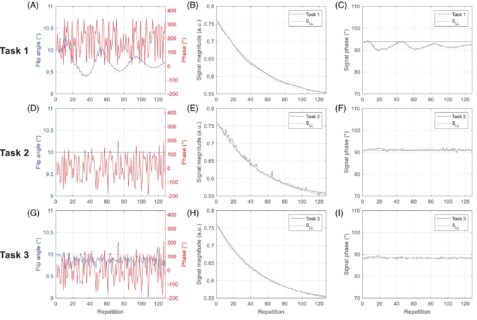
Many MRI measurements rely on fast readout of a prepared magnetization state. As preparation takes time and the readout ‘destroys’ this magnetization state. Such prepared MRI is time demanding.
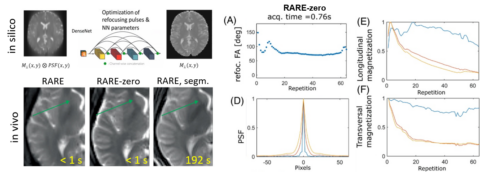
In CEST we also want to acquire many differently prepared CEST images to extract certain peaks or quantitative parameters. Thus, a fast readout after prepration is necessary to reduce overall scan time. My group develops the most extreme case of this fast readouts, which is a single 3D whole brain snapshot after a single preparation. This is possible with accelerated GRE and EPI readouts and provides one of the fastest CEST methods.
3. Ultra High Field (UHF) Imaging
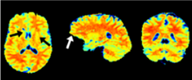
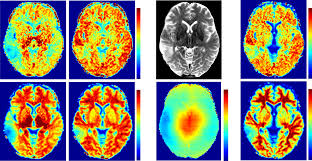
At UHF the MRI signal is generally higher and also the spectral selectivity increases. Both are especially beneficial for CEST imaging, however, it comes at a cost of stronger field inhomogeneities. My group develops novel methods to mitigate and compensate these field inhomogeneities as well as patient movement during the acquisition. Only after correction reliable high quality spectra and contrast maps can be generated. We work on 7 T and 9.4 T human UHF MRI scanners.
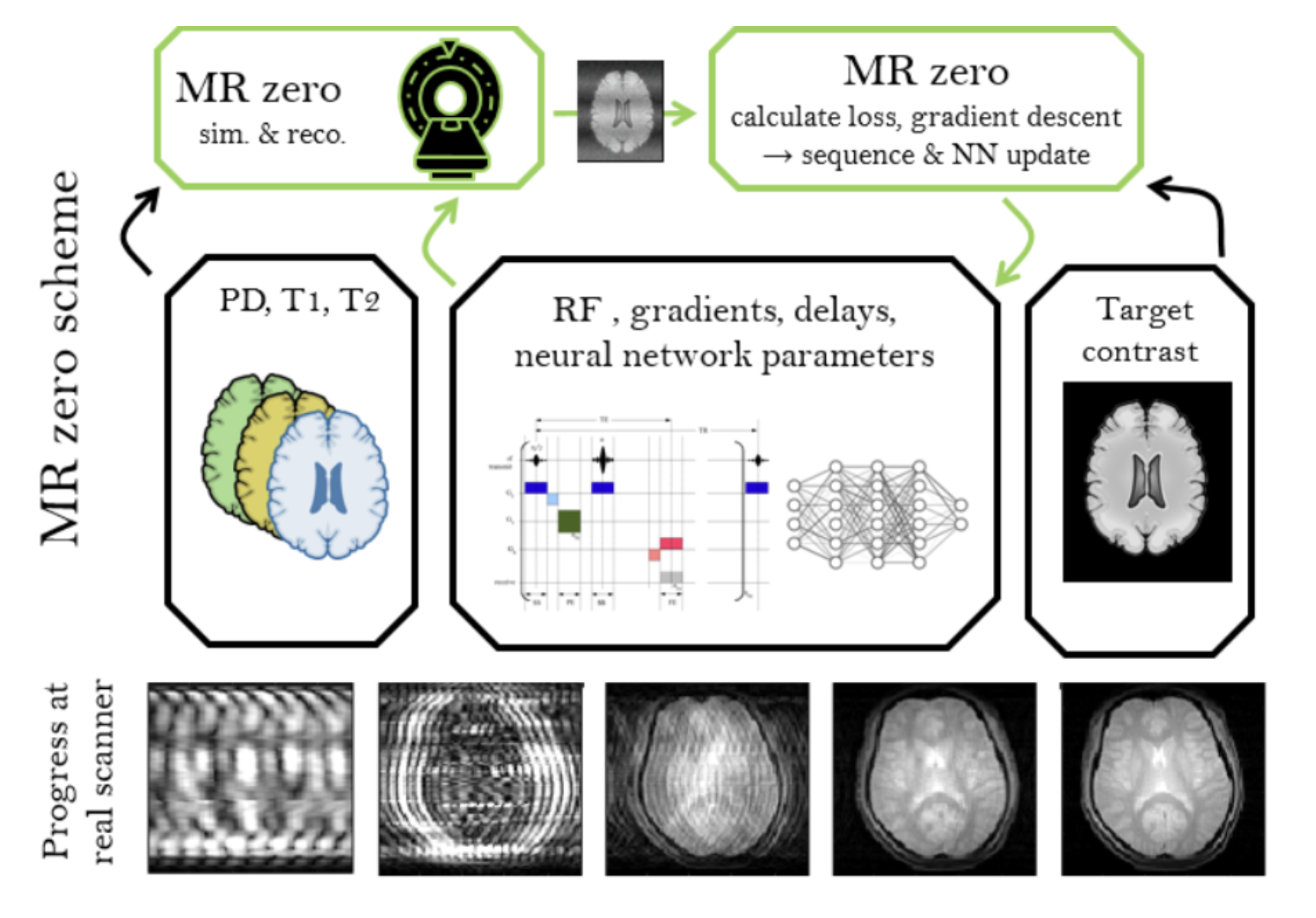
4. Self-Learning MRI
In January 2018 (9.1.) we asked ourselves:
“What if MRI sequence programming is just a game that we can win like winning Go using reinforced learning?
The rules are the Bloch equations. The sequence is our strategy. The k-space is our feature extraction. And the difference to the correct image is the cost function.”
Since then, we experimented to generate a prototype for a self-learning MRI, which works now for simple problems in 2D and low resolution. If we can scale this to high resolution and 3D, a new MRI method development paradigm would be reached. Generating an MR sequence and reconstruction would be solely based on the target provided, which can be a certain MR contrast; but the possibilities for targets are limitless, e.g. quantification, segmentation, as well as contrasts of other imaging modalities.